Business Cycle Decomposition of Canadian GDP Using HP Filter
🔍 One of the major goals of modern macroeconomics is to understand how shocks affect the economy and how their effects propagate over time.
But explaining these dynamics remains a challenge—even for experts. As any microeconomist will tell you: sometimes, explaining what an instrumental variable is to a non-economist is harder than the econometrics behind it! 😅
📉 The Reality Behind GDP
GDP doesn’t follow a straight path. It fluctuates, reacts, and deviates—these are business cycles.
Understanding these fluctuations is essential to:
- anticipate crises,
- design effective public policies, and
- guide informed economic decisions.
I illustrated this by decomposing Canadian GDP using the Hodrick–Prescott filter, which separates:
- Trend (long-term growth path)
- Cycle (short-term deviations from trend)
📊 Visualization
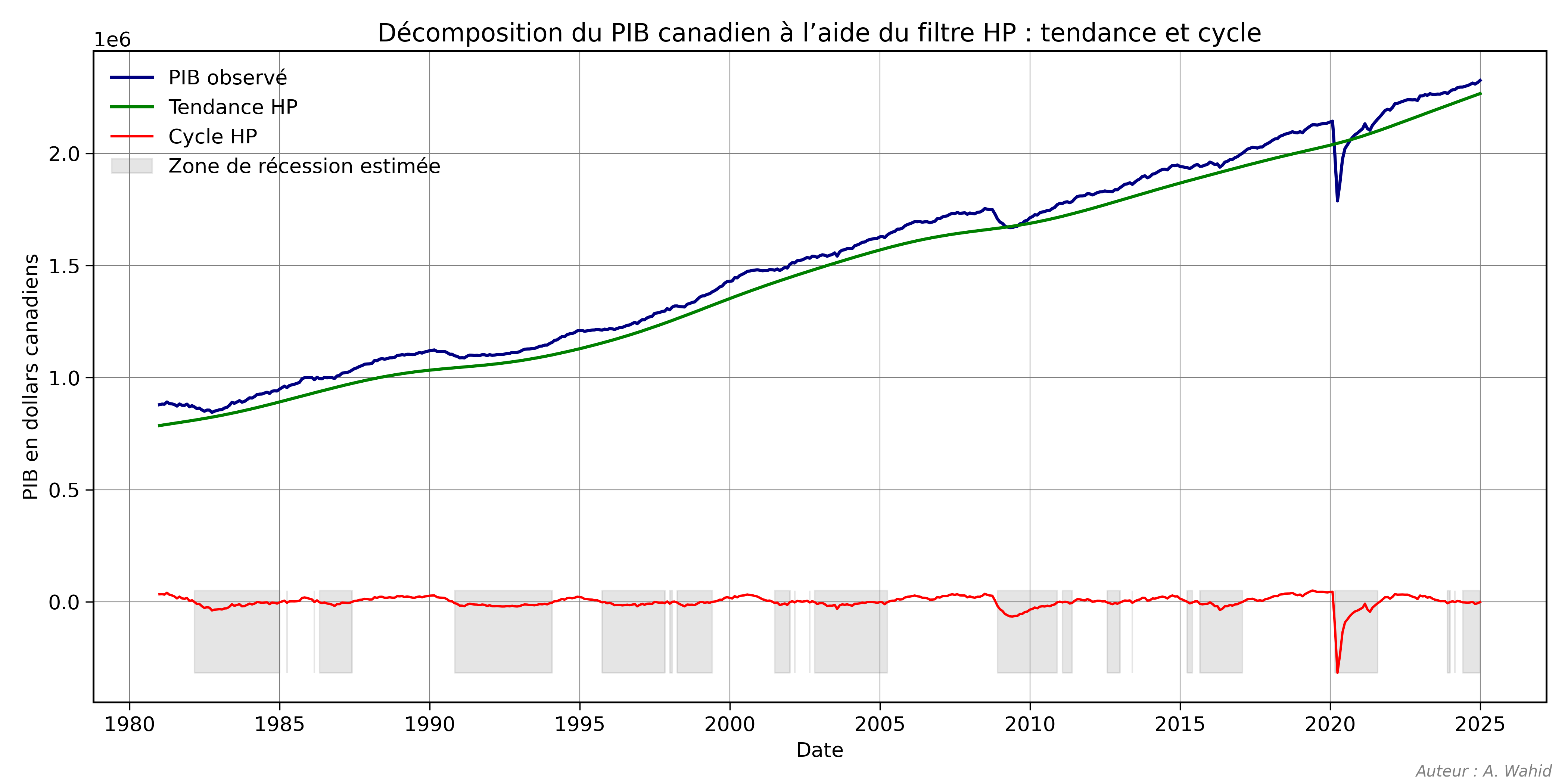
Legend:
- Blue: Observed GDP
- Green: HP Trend
- Red: HP Cycle
- Gray zones: Estimated recession periods
🧰 Methodology & Data
- Method: Hodrick–Prescott filter (HP Filter)
- Data source: Chaire en macroéconomie et prévisions (CMP), Canada
- Tools used: Python (
pandas,statsmodels,matplotlib)
🧠 Why It Matters
Whether in cooking, medicine, or macroeconomics—precision matters.
- In cooking: a wrong dose can ruin the dish.
- In medicine: a milligram too much can have serious consequences.
- In macroeconomics: misjudging a shock or reacting late can cost thousands of jobs or worsen a recession.
📚 Suggested Readings
- Blanchard, O. (2025) — Convergence? Thoughts about the Evolution of Macroeconomics
- Ramey, V. (2016) — Macroeconomic Shocks and Their Propagation, Handbook of Macroeconomics, Vol. 2, Chap. 2
🏷️ Tags
#Macroeconomics, #HPFilter, #BusinessCycle, #EconomicPolicy, #CanadaGDP, #Python, #TimeSeries, #Blanchard, #Ramey, #NBER
